What is the relationship between radiation dose and its effects on human body?
Ionizing radiation can cause damage to living cells and tissues. Its effects depend on the intensity of the radiation, exposure time and the kind of body cells affected.
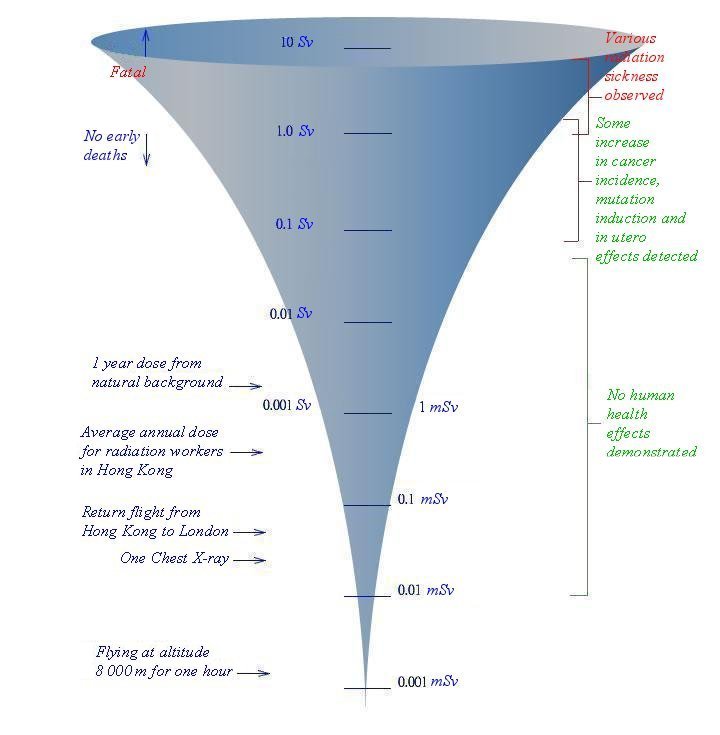
When human body receives a high radiation dose of more than 1 Sv in a short time, acute radiation effects may occur, such as nausea, vomiting, fatigue and epilation. The result may be fatal if radiation dose is 10 Sv or more with no suitable medical treatments. In addition, radiation can increase the risk of cancer and genetic mutation.
Though the level is very low, the general public receive radiation dose from the natural environment day and night. Even for the radiation workers, the estimated fatal risk due to radiation is still below the average risk among other fatal factors. The following table shows some common risk factors for the Hong Kong populations.
| Fatal factors | Annual fatal risk |
|---|---|
| Smoking (10 cigarette per day) | 1/2001 |
| Malignancy | 1/6302 |
| Occupational accidents | 1/550003 |
| Traffic accidents | 1/222002 |
| Local radiation worker (around 0.11 mSv per year)5 | 1/2840914 |
- "Living with Radiation" published by the National Radiological Protection Board, UK (1998)
- Annual Report 1997/98, Department of Health
- Report of the Commissioner for Labour, 1997
- Risk factor was taken as 3.2 x 10-5 per mSv (estimated from ICRP Publication 103, 2007)
- "Occupational Exposure in Hong Kong 2017", Department of Health
Effects of radiation